In the realm of medical advancements, CPT full thickness skin grafts emerge as a groundbreaking technique, offering hope for restoring damaged skin and improving patients’ lives. Join us as we delve into the fascinating world of FTSG, exploring its intricacies, applications, and post-operative care.
This comprehensive guide will provide you with a clear understanding of FTSG, empowering you with the knowledge you need to make informed decisions about your healthcare.
Full-Thickness Skin Graft (FTSG)
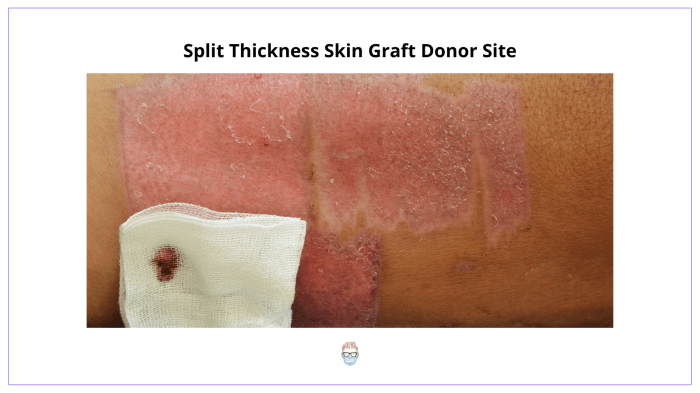
A full-thickness skin graft (FTSG) is a surgical procedure that involves removing a section of skin from one part of the body (the donor site) and transplanting it to another part of the body (the recipient site) to replace damaged or missing skin.
The purpose of an FTSG is to restore function and improve the appearance of the affected area.
Types of FTSG
There are two main types of FTSGs:
- Split-thickness skin graft (STSG):In this procedure, only the top layers of the skin are removed from the donor site. STSGs are typically used to cover large areas of skin loss.
- Full-thickness skin graft (FTSG):In this procedure, the entire thickness of the skin is removed from the donor site. FTSGs are typically used to cover smaller areas of skin loss and provide a more natural-looking result.
Indications and Contraindications for FTSG
FTSGs are indicated for a variety of conditions, including:
- Burns
- Traumatic injuries
- Skin cancer
- Birth defects
FTSGs are contraindicated in patients with:
- Active infection at the donor or recipient site
- Poor circulation to the recipient site
- A history of keloid formation
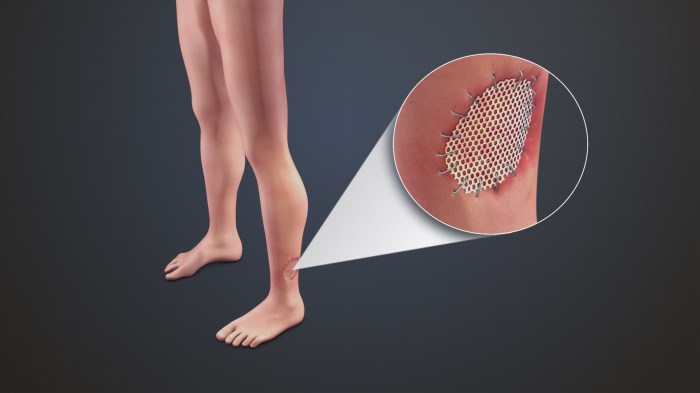
Procedure for FTSG
Full-thickness skin grafting (FTSG) is a surgical procedure that involves transplanting a section of healthy skin from one area of the body (the donor site) to another area (the recipient site) to replace damaged or missing skin. The procedure is typically performed to treat severe burns, traumatic injuries, or skin defects.
Preparing the Donor and Recipient Sites
Before the grafting procedure, both the donor and recipient sites are carefully prepared. The donor site is typically chosen from an area with healthy, excess skin, such as the thigh or abdomen. The recipient site is the area where the damaged or missing skin needs to be replaced.
The donor site is shaved and cleaned, and the recipient site is debrided (cleaned of any dead or damaged tissue). The recipient site is then prepared to receive the graft by creating a bed of granulation tissue, which is a type of new tissue that forms over the wound.
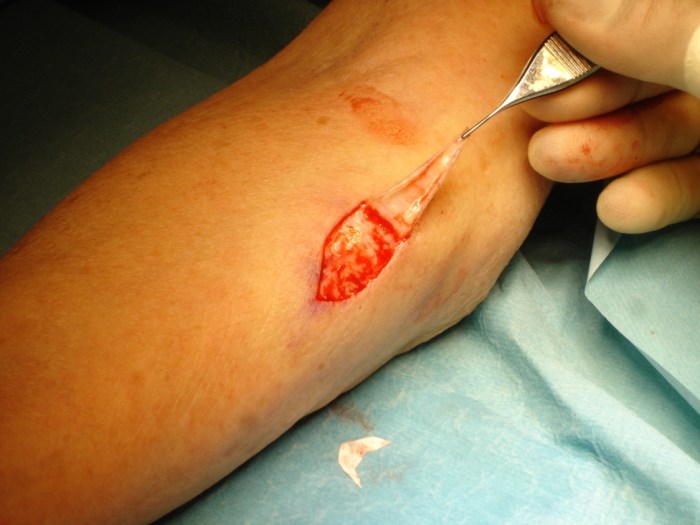
Harvesting and Grafting the Skin
Once the donor and recipient sites are prepared, the skin graft is harvested from the donor site. This is done using a scalpel or a dermatome, a specialized tool that removes a thin layer of skin. The harvested skin is then carefully placed over the recipient site and secured with sutures or staples.
The grafted skin will typically take several weeks to heal and integrate with the surrounding tissue. During this time, the graft is monitored closely to ensure that it is healing properly and that there are no signs of infection.
Post-Operative Care for FTSG
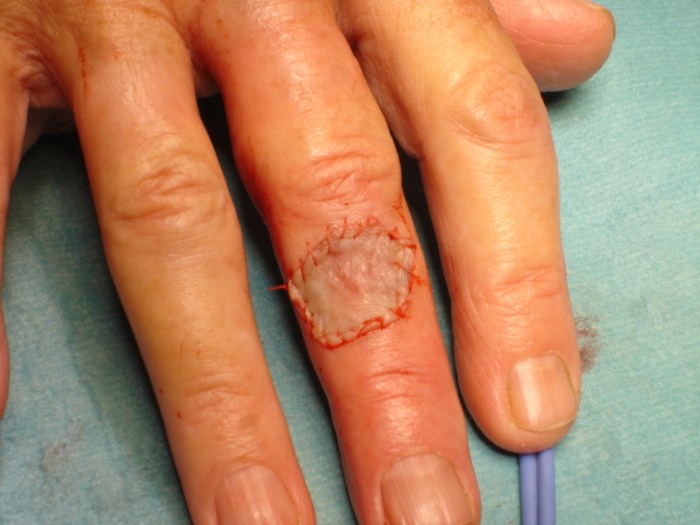
Following FTSG surgery, proper post-operative care is crucial to ensure optimal healing and prevent complications. This care involves wound care, infection prevention, and monitoring for potential issues.
CPT full thickness skin graft involves transplanting a full layer of skin from one area to another to treat burns, wounds, or skin defects. If you’re studying Spanish, you might find the AP Spanish Temas textbook PDF helpful for language learning.
The comprehensive guide can enhance your understanding of grammar, vocabulary, and cultural aspects, complementing your knowledge of CPT full thickness skin graft.
Wound Care
The surgical site must be kept clean and dry to promote healing. Regular wound dressings and daily cleansing are essential. The type of dressing used will depend on the size and location of the graft. Non-adherent dressings or foams are commonly used to protect the graft and absorb any drainage.
Infection Prevention
Infection is a major concern after FTSG. Antibiotics may be prescribed to prevent or treat infections. Patients should monitor the wound for signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or drainage. Early detection and treatment are crucial to prevent serious complications.
Potential Complications
While FTSG is generally a successful procedure, certain complications can occur. These include:
- Graft failure: The graft may not adhere to the recipient site or may become necrotic (die).
- Infection: Infection can develop in the graft or surrounding tissues.
- Hematoma: Blood can accumulate beneath the graft, causing swelling and pain.
- Hypertrophic scarring: The scar may become raised and thickened.
- Contracture: The graft may shrink and cause the surrounding skin to contract.
Applications of FTSG
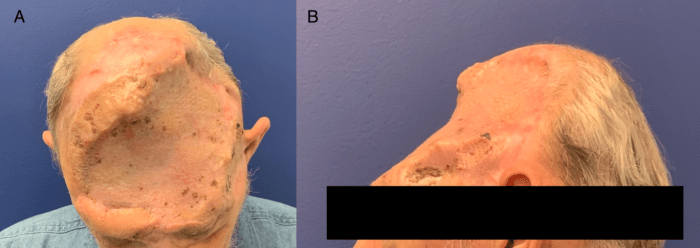
Full-thickness skin grafts (FTSGs) are used to treat a variety of skin defects, including burns, wounds, and congenital abnormalities. FTSGs are often used in cases where other skin grafting techniques, such as split-thickness skin grafts (STSGs), are not suitable.
FTSGs are particularly useful for treating burns, as they can provide a durable and functional skin covering. FTSGs are also used to treat wounds that have failed to heal with other methods, such as pressure ulcers and diabetic foot ulcers.
In addition, FTSGs can be used to correct congenital abnormalities, such as cleft lip and palate.
Advantages of FTSG, Cpt full thickness skin graft
- FTSGs provide a durable and functional skin covering.
- FTSGs are less likely to contract than STSGs.
- FTSGs can be used to treat a variety of skin defects.
Disadvantages of FTSG
- FTSGs are more difficult to harvest than STSGs.
- FTSGs can be more painful than STSGs.
- FTSGs can leave a visible scar.
FAQ Overview: Cpt Full Thickness Skin Graft
What is the purpose of a CPT full thickness skin graft?
A CPT full thickness skin graft is used to replace damaged or lost skin with healthy tissue from another part of the body.
What are the different types of CPT full thickness skin grafts?
There are two main types of CPT full thickness skin grafts: split-thickness skin grafts and full-thickness skin grafts.
What are the indications for a CPT full thickness skin graft?
CPT full thickness skin grafts are indicated for the treatment of burns, wounds, and other skin defects that cannot be closed with other methods.
What are the contraindications for a CPT full thickness skin graft?
CPT full thickness skin grafts are contraindicated in patients with active infection, poor circulation, or other medical conditions that may impair wound healing.