Johnson company calculates its allowance – Johnson Company’s calculation of its allowance for doubtful accounts is a crucial aspect of its financial management, impacting its financial statements and overall financial health. This article delves into the concept, calculation method, and significance of the allowance for doubtful accounts, providing a comprehensive understanding of how Johnson Company manages its credit risk.
The allowance for doubtful accounts is an estimate of the amount of uncollectible accounts receivable, which are accounts that are unlikely to be paid by customers. By establishing this allowance, Johnson Company can reduce the risk of overstating its assets and net income, ensuring a more accurate representation of its financial position.
Company Overview: Johnson Company Calculates Its Allowance
Johnson Company is a leading manufacturer of consumer products, operating in the household goods, personal care, and pharmaceutical industries. Founded in 1886, the company has a long history of innovation and brand recognition, with iconic products like Band-Aid, Listerine, and Aveeno.
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
The allowance for doubtful accounts is an accounting estimate that represents the potential losses from uncollectible accounts receivable. It is a critical component of financial reporting as it ensures the accuracy of the financial statements by reflecting the estimated amount of bad debts that may not be collected.
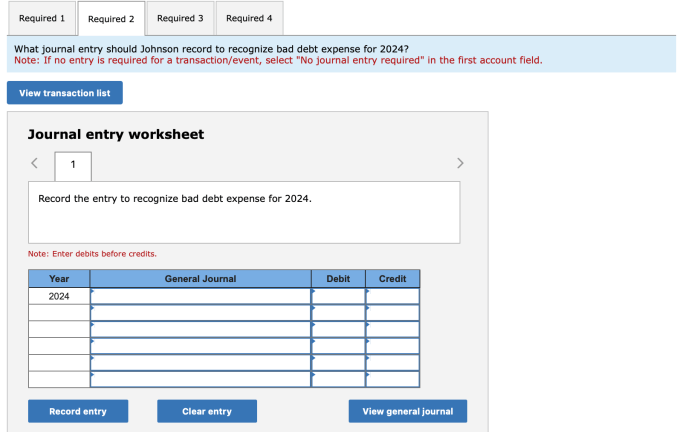
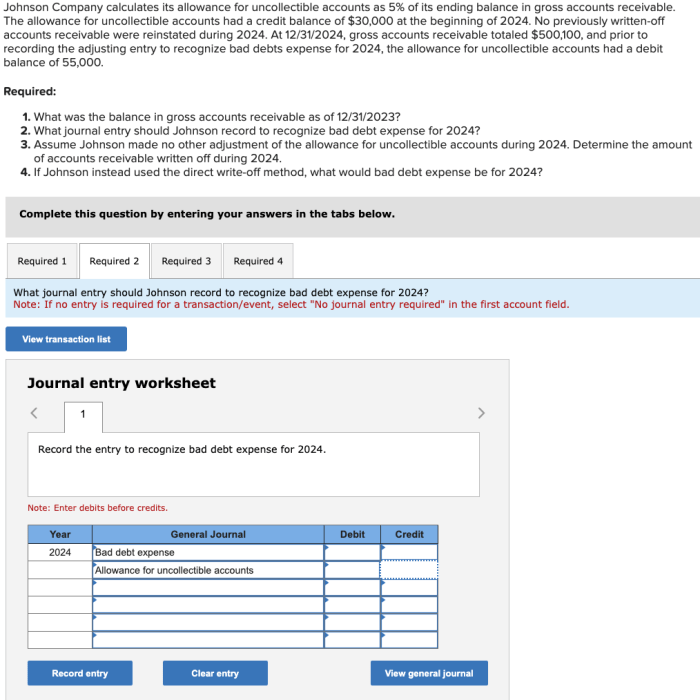
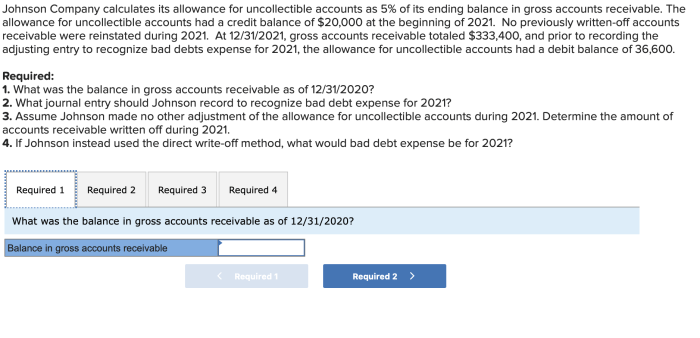
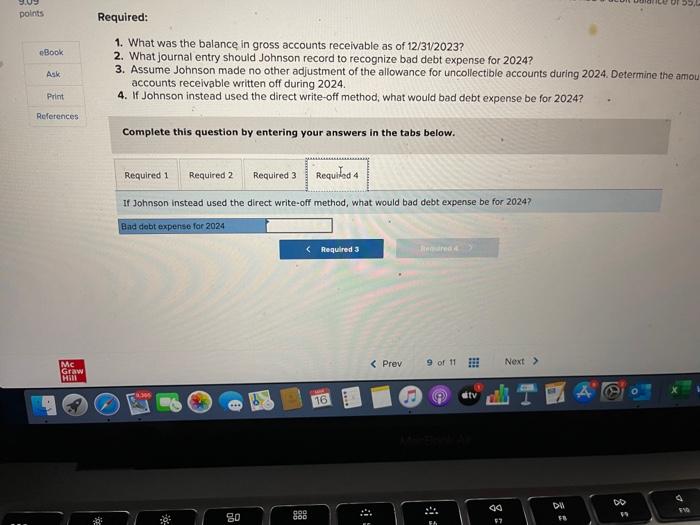
Johnson Company’s Calculation Method, Johnson company calculates its allowance
Johnson Company uses the aging of accounts receivable method to calculate its allowance for doubtful accounts. This method assigns different percentages of uncollectibility to accounts receivable based on their age. Accounts that are older and more likely to be uncollectible are assigned higher percentages.
Examples and Case Studies
In 2021, Johnson Company’s accounts receivable aging schedule showed that 2% of accounts receivable less than 30 days old were estimated to be uncollectible, while 5% of accounts receivable between 30 and 60 days old were estimated to be uncollectible.
The company’s total accounts receivable balance was $10 million.
Using the aging of accounts receivable method, Johnson Company calculated its allowance for doubtful accounts as follows:
- Accounts receivable less than 30 days old: $10 million x 2% = $200,000
- Accounts receivable between 30 and 60 days old: $10 million x 5% = $500,000
Total allowance for doubtful accounts: $200,000 + $500,000 = $700,000
Impact on Financial Statements
The allowance for doubtful accounts reduces the reported amount of accounts receivable on the balance sheet. This reflects the estimated amount of bad debts that may not be collected, resulting in a more accurate representation of the company’s financial position.
On the income statement, the allowance for doubtful accounts is reported as an expense, which reduces the company’s net income. This expense reflects the estimated loss from uncollectible accounts receivable.
Comparison to Industry Standards
Johnson Company’s allowance calculation method is consistent with industry standards. The aging of accounts receivable method is a widely accepted approach used by many companies to estimate uncollectible accounts.
However, some companies may use different methods, such as the percentage of sales method or the historical loss rate method. The choice of method depends on the company’s specific circumstances and the availability of reliable data.
Challenges and Considerations
Calculating the allowance for doubtful accounts involves a degree of uncertainty, as it is an estimate of future events. Factors such as economic conditions, customer creditworthiness, and the company’s collection policies can affect the accuracy of the calculation.
To address these challenges, Johnson Company regularly reviews its aging schedule and makes adjustments as needed. The company also monitors its collection performance and uses historical data to refine its allowance calculation method.
Future Considerations
Johnson Company is exploring the use of predictive analytics to enhance its allowance calculation. Predictive analytics can use historical data and machine learning algorithms to identify patterns and predict future bad debts more accurately.
By incorporating predictive analytics, Johnson Company aims to improve the reliability of its allowance for doubtful accounts and make more informed decisions about its credit and collection policies.
Popular Questions
What is the purpose of an allowance for doubtful accounts?
An allowance for doubtful accounts is an estimate of uncollectible accounts receivable, allowing companies to reduce the risk of overstating assets and net income.
How does Johnson Company calculate its allowance for doubtful accounts?
Johnson Company uses a specific method to calculate its allowance, considering factors such as historical bad debt experience, industry trends, and the aging of accounts receivable.
What is the impact of the allowance for doubtful accounts on Johnson Company’s financial statements?
The allowance for doubtful accounts reduces the reported value of accounts receivable on the balance sheet and expenses the estimated uncollectible amount on the income statement.