The root type assigned for a mammography is a crucial aspect of breast imaging, providing valuable insights into the structure and composition of breast tissue. This comprehensive guide delves into the various root type classifications, imaging techniques, and clinical implications, empowering healthcare professionals with the knowledge to optimize patient care.
Mammography, a widely used screening tool for breast cancer detection, relies on the assessment of breast tissue density. The root type, a measure of breast tissue density, plays a significant role in interpreting mammographic findings and guiding treatment decisions. Understanding the root type assigned for a mammogram is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective patient management.
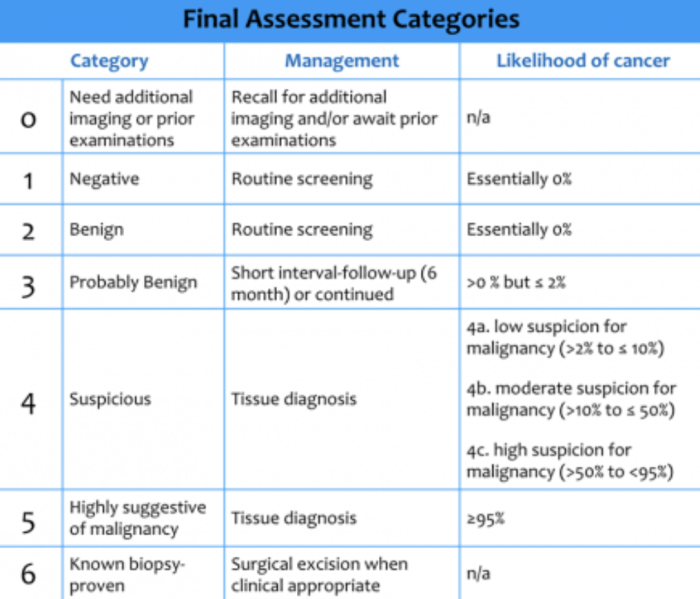
Root Type Classifications: The Root Type Assigned For A Mammography Is
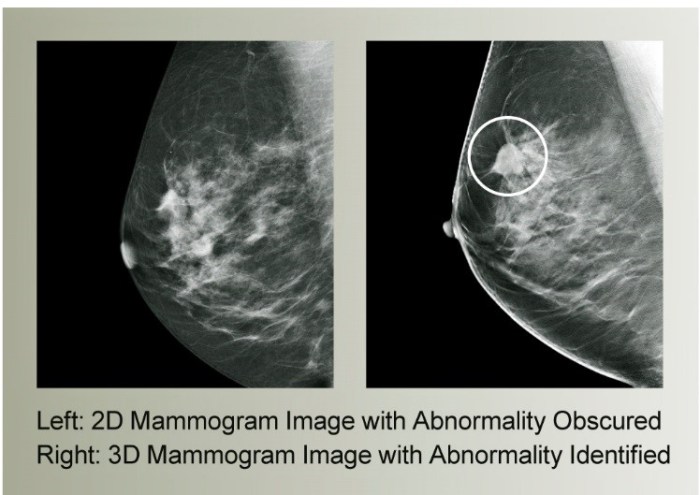
The root type assigned for a mammogram plays a crucial role in guiding patient care and treatment decisions. Mammograms are categorized into different root types based on the appearance and characteristics of the breast tissue, with each type indicating a specific level of risk and management approach.
Imaging Techniques
Various imaging techniques are employed to determine the root type assigned for a mammogram. These include:
- Full-field Digital Mammography (FFDM):FFDM uses low-energy X-rays to create detailed images of the breast, providing a clear visualization of breast tissue and any potential abnormalities.
- Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT):DBT takes multiple X-ray images of the breast at different angles, allowing for a three-dimensional reconstruction of the breast tissue. This technique offers improved sensitivity and specificity in detecting breast cancer.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI):MRI uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to generate detailed images of the breast, particularly useful for dense breast tissue and detecting small lesions that may not be visible on mammograms.
Clinical Significance, The root type assigned for a mammography is
The root type assigned for a mammogram has significant clinical implications for patient care. Different root types are associated with varying levels of breast cancer risk and require tailored management strategies:
- Type 1:Lowest risk of breast cancer, typically characterized by abundant fatty tissue and no dense areas.
- Type 2:Intermediate risk, with scattered areas of dense tissue.
- Type 3:Higher risk, with heterogeneously dense tissue throughout the breast.
- Type 4:Highest risk, with extremely dense breast tissue that may obscure underlying abnormalities.
Reporting and Interpretation
The reporting and interpretation of the root type assigned for a mammogram follow specific guidelines:
| Root Type | Imaging Technique | Clinical Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Type 1 | FFDM, DBT, MRI | Low risk of breast cancer |
| Type 2 | FFDM, DBT | Intermediate risk |
| Type 3 | FFDM, DBT, MRI | Higher risk |
| Type 4 | FFDM, DBT, MRI | Highest risk |
FAQ Insights
What are the different root type classifications?
Root type classifications range from 1 to 4, with 1 indicating the lowest density and 4 indicating the highest density.
How is the root type determined?
The root type is determined by analyzing the mammographic image and assessing the proportion of dense tissue to fatty tissue.
What are the clinical implications of root type?
Root type can influence the risk of breast cancer, the sensitivity of mammographic screening, and the choice of treatment options.