On a processed radiograph dental caries appear as – On a processed radiograph, dental caries appear as… Embark on a journey of discovery as we delve into the captivating world of dental caries and their telltale signs on radiographs. This comprehensive guide unravels the mysteries of caries detection, empowering you with the knowledge to accurately interpret these crucial images.
Uncover the characteristic radiographic features of dental caries, deciphering their appearance at various stages of progression. Explore the intricate interplay of factors that influence their radiographic presentation, including projection angles, radiation exposure, patient positioning, and image processing techniques.
Radiographic Appearance of Dental Caries: On A Processed Radiograph Dental Caries Appear As
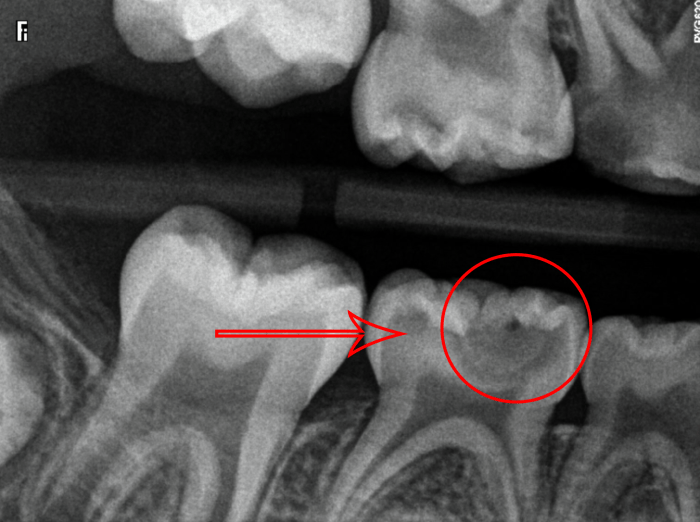
Dental caries, commonly known as tooth decay, is a prevalent oral health issue. Radiographs play a crucial role in detecting and diagnosing caries, providing valuable information about the extent and severity of the condition. On a processed radiograph, caries appear as radiolucent areas due to the demineralization of tooth structure.The
radiographic appearance of caries varies depending on the stage of progression. Incipient caries, the earliest stage, manifests as a faint radiolucency within the enamel. As caries progress into the dentin, the radiolucency becomes more pronounced and extends towards the pulp.
In advanced caries, the radiolucency may reach the pulp chamber, indicating extensive damage to the tooth.
Factors Influencing Radiographic Appearance
The radiographic appearance of dental caries can be influenced by several factors:
Projection angle
The angle at which the X-ray beam is directed towards the tooth can affect the visibility of caries. Optimal angulation is crucial for detecting caries in specific areas.
Radiation exposure
The amount of radiation used during radiography can impact the contrast and detail of the resulting image. Proper exposure settings are necessary to minimize radiation exposure while ensuring adequate image quality.
Patient positioning
The patient’s positioning during radiography can influence the clarity of the image. Proper head and tooth positioning helps align the structures of interest, reducing image distortion and improving caries detection.
Image processing techniques
Digital image processing techniques, such as contrast enhancement and edge detection, can improve the visibility of caries on radiographs. These techniques can enhance subtle radiolucencies, aiding in the early detection of caries.
Differential Diagnosis
It is important to differentiate dental caries from other radiographic findings that may resemble caries. These include:
Anatomical structures
Normal anatomical structures, such as pulp horns and developmental grooves, can sometimes be mistaken for caries. Careful examination of the surrounding structures and comparison with contralateral teeth can help differentiate between caries and normal anatomy.
Restorations
Dental restorations, such as amalgam fillings and composite resin restorations, can appear radiopaque on radiographs. However, restorations typically have well-defined margins and do not exhibit the progressive radiolucency characteristic of caries.
Artifacts
Artifacts, such as scratches or air bubbles, can mimic the appearance of caries on radiographs. Careful examination of the image and correlation with clinical findings can help distinguish artifacts from actual caries.
Clinical Significance
Accurately detecting and interpreting dental caries on radiographs is crucial for effective patient management. Early detection allows for prompt intervention and treatment, preventing further progression of the disease. Radiographs help dentists assess the extent and severity of caries, plan appropriate treatment options, and monitor the progress of treatment.
| Radiographic Appearance | Clinical Significance |
|---|---|
| Incipient caries | Early stage, minimal damage, reversible with preventive measures |
| Moderate caries | Dentin involvement, requires restorative treatment |
| Advanced caries | Extensive damage, may require root canal treatment or extraction |
Advanced Imaging Techniques, On a processed radiograph dental caries appear as
Advanced imaging techniques have been developed to enhance the detection and diagnosis of dental caries:
Cone beam computed tomography (CBCT)
CBCT provides three-dimensional images of the teeth and surrounding structures, allowing for more accurate assessment of caries extent and proximity to vital structures.
Digital subtraction radiography
This technique involves subtracting a previous radiograph from a current one, highlighting changes in tooth structure and improving caries detection.
Laser fluorescence imaging
This technique uses laser light to excite dental caries, which emit a characteristic fluorescence that can be captured and analyzed to detect caries at an early stage.
Query Resolution
How do dental caries appear on a processed radiograph?
On a processed radiograph, dental caries typically manifest as radiolucent areas, indicating demineralized tooth structure.
What factors influence the radiographic appearance of dental caries?
Factors such as projection angle, radiation exposure, patient positioning, and image processing techniques can affect the visibility and characteristics of caries on radiographs.
How can we differentiate dental caries from other radiographic findings?
Careful analysis of radiographic features, including shape, location, and surrounding structures, helps differentiate caries from anatomical structures, restorations, and artifacts.
What is the clinical significance of accurately detecting dental caries on radiographs?
Early and accurate caries detection on radiographs enables timely intervention, preventing disease progression and preserving tooth integrity.