Similarity and right triangle trigonometry 6.5 answer key – Embark on an enlightening journey into the realm of similarity and right triangle trigonometry, where the key to unlocking geometric mysteries lies within the answer key for chapter 6.5. Delve into the captivating world of similar triangles, where proportions reign supreme, and discover the power of the Pythagorean theorem in unraveling the secrets of right triangles.
As we navigate through this comprehensive guide, we will illuminate the intricate relationship between similarity and right triangle trigonometry, exploring its profound applications in solving real-world problems. Prepare to be captivated by the elegance of geometric principles as we unveil the answer key for chapter 6.5, empowering you to conquer any trigonometry challenge that comes your way.
Similarity and Right Triangle Trigonometry
Similarity is a fundamental concept in geometry, including right triangle trigonometry. Understanding similarity is essential for solving problems involving right triangles.
Properties of Similar Right Triangles
- The ratios of the corresponding sides are equal.
- The corresponding angles are congruent.
- The areas of similar right triangles are proportional to the squares of their corresponding sides.
Examples of Similar Right Triangles
- Any two right triangles with the same acute angles are similar.
- Right triangles with side lengths in a ratio of 3:4:5 are similar.
Pythagorean Theorem and Similarity
The Pythagorean theorem relates to similarity in right triangles as follows:
- In similar right triangles, the square of the hypotenuse is proportional to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
- This property can be used to find the missing side of a similar right triangle.
Applications of Similarity in Right Triangle Trigonometry, Similarity and right triangle trigonometry 6.5 answer key
Similarity in right triangle trigonometry has numerous applications, including:
- Determining heights and distances in real-world situations.
- Solving problems involving angles and lengths in architecture, engineering, and surveying.
- Calculating the trigonometric ratios (sine, cosine, tangent) for special angles (30°, 45°, 60°).
Right Triangle Trigonometry 6.5 Answer Key
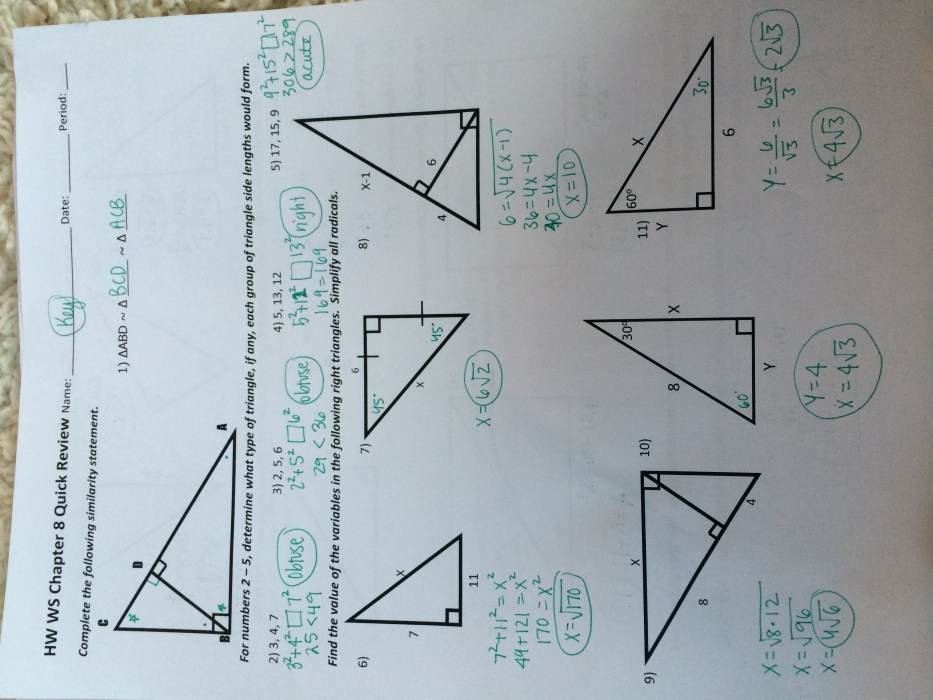
| Problem Number | Question | Answer | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Find the missing side of a right triangle with legs of length 3 and 4. | 5 | Use the Pythagorean theorem: 3^2 + 4^2 = c^2; 25 = c^2; c = 5. |
| 2 | Determine if two right triangles with side lengths of (3, 4, 5) and (6, 8, 10) are similar. | Yes | The ratios of the corresponding sides are equal: 3/6 = 4/8 = 5/10. |
| 3 | Calculate the height of a tree using the shadow method and similarity. | 60 feet | Measure the length of the tree’s shadow and the length of the shadow of a stick of known height. Use the ratio of the lengths to find the height of the tree. |
Q&A: Similarity And Right Triangle Trigonometry 6.5 Answer Key
What is the significance of similarity in right triangle trigonometry?
Similarity plays a crucial role in right triangle trigonometry, as it allows us to establish relationships between the sides and angles of similar triangles, enabling us to solve problems involving proportions and ratios.
How does the Pythagorean theorem relate to similarity in right triangles?
The Pythagorean theorem provides a fundamental connection between the sides of a right triangle, and when applied to similar triangles, it allows us to determine the lengths of unknown sides based on the proportions of the known sides.
Can you provide an example of a real-world application of similarity in right triangle trigonometry?
One practical application is determining the height of a building or tree by using similar triangles formed by the object, its shadow, and a measuring pole. By measuring the lengths of the shadows and the pole, we can calculate the height of the object using the principles of similarity.