When it comes to understanding your paycheck, the reading a pay stub answer key is your ultimate guide. This comprehensive resource provides a clear and concise overview of the key sections and components of a pay stub, empowering you to analyze and interpret your earnings, deductions, and net pay with confidence.
Whether you’re a seasoned employee or just starting out, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and skills to decipher your pay stub and make informed financial decisions. So, let’s dive into the world of pay stubs and unlock the secrets to financial literacy.
Understanding Pay Stubs
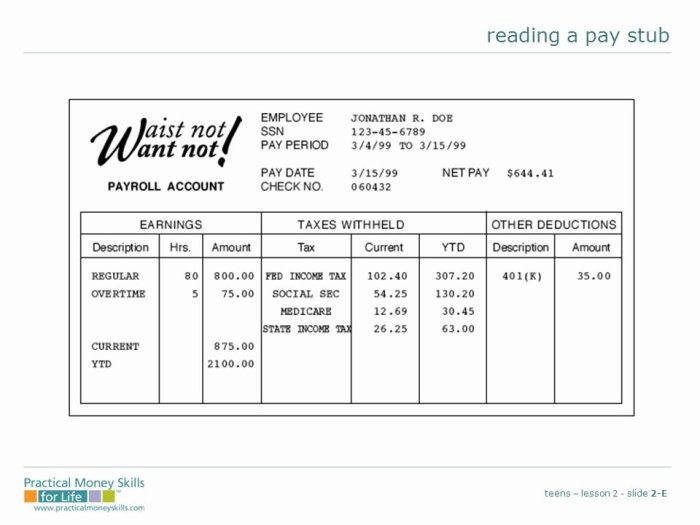
A pay stub, also known as a paycheck stub or earnings statement, is a document that provides detailed information about an employee’s earnings and deductions for a specific pay period. It serves as an official record of the employee’s compensation and serves several important purposes:
- Verification of Earnings:Pay stubs provide a clear breakdown of an employee’s gross pay, which includes all earnings before deductions, as well as net pay, which is the amount of money the employee actually receives after deductions.
- Documentation for Taxes and Benefits:Pay stubs contain information about taxes withheld, such as federal income tax, Social Security tax, and Medicare tax. They also show deductions for benefits such as health insurance, retirement contributions, and union dues.
- Proof of Income:Pay stubs can be used as proof of income for various purposes, such as applying for loans, renting an apartment, or obtaining government assistance.
Key Sections and Components of a Pay Stub
Pay stubs typically include the following key sections and components:
- Employee Information:This section includes the employee’s name, address, and employee ID number.
- Pay Period:This section indicates the start and end dates of the pay period.
- Gross Earnings:This section lists all of the employee’s earnings for the pay period, including regular wages, overtime pay, bonuses, and commissions.
- Deductions:This section lists all of the deductions taken from the employee’s gross earnings, such as taxes, health insurance premiums, and retirement contributions.
- Net Pay:This section shows the amount of money the employee receives after all deductions have been taken out.
Common Pay Stub Formats
There are several common pay stub formats used by employers:
- Traditional Pay Stub:This format is the most common and includes all of the key sections and components listed above.
- Simplified Pay Stub:This format is more concise and may only include the most essential information, such as gross earnings, net pay, and deductions.
- Online Pay Stub:Many employers now offer online pay stubs that employees can access through a secure website or mobile app.
Reading Pay Stub Components: Reading A Pay Stub Answer Key
Understanding your pay stub is crucial for managing your finances effectively. Let’s delve into the key components of a pay stub.
Earnings
Earnings typically include:
-
-*Regular Pay
Compensation for hours worked at the standard rate.
-*Overtime Pay
Extra pay for hours worked beyond the standard workweek.
-*Bonuses
Additional payments for meeting performance goals or special achievements.
-*Commissions
Earnings based on sales or other performance metrics.
Deductions and Withholdings
Deductions and withholdings reduce your gross pay before taxes are calculated. These may include:
-
-*Pre-Tax Deductions
Contributions to retirement accounts (e.g., 401(k), IRA) or other employee-elected benefits (e.g., health insurance premiums).
-*Post-Tax Deductions
Contributions to non-retirement accounts or other voluntary expenses (e.g., union dues, charity donations).
-*Withholdings
Taxes withheld from your paycheck, including federal income tax, Social Security tax, and Medicare tax.
Net Pay and Take-Home Pay
Net Pay: Gross pay minus deductions and withholdings. This is the amount you receive before any additional taxes or deductions are taken out.Take-Home Pay: Net pay minus any additional deductions or taxes (e.g., state income tax, garnishments). This is the actual amount of money you receive in your bank account.Understanding
net pay and take-home pay is essential for budgeting and financial planning.
Analyzing Pay Stubs
Understanding your pay stub is crucial for ensuring accuracy and keeping track of your earnings. Here’s a step-by-step process to analyze your pay stub effectively:
Review Basic Information
Start by verifying the basic information, such as your name, employee ID, pay period, and hours worked. Ensure that these details are correct and match your employment records.
Earnings
Check your gross earnings, which include your regular pay, overtime, bonuses, and any other taxable income. Make sure the amounts align with your expected earnings for the pay period.
Deductions
Review your deductions carefully. Common deductions include federal and state taxes, Social Security, Medicare, health insurance, and retirement contributions. Verify that the amounts deducted are correct and align with your withholding elections.
Net Pay
Calculate your net pay by subtracting deductions from your gross earnings. This is the amount you will receive as your take-home pay.
Potential Errors or Discrepancies
Look out for any errors or discrepancies, such as:
- Incorrect hours worked
- Miscalculated overtime pay
- Inaccurate tax withholdings
- Missing or incorrect deductions
Tracking Changes
Compare your pay stubs over time to track changes in your earnings, deductions, and net pay. This can help you identify trends and potential issues.
Using Pay Stubs for Financial Planning
Pay stubs offer a wealth of information that can empower you to make informed financial decisions. By understanding your income and expenses, you can create a budget that aligns with your financial goals.
Creating a Budget
- Track your income and expenses for a month to establish a baseline.
- Categorize your expenses into essential (e.g., housing, food), discretionary (e.g., entertainment, dining out), and savings.
- Allocate a portion of your income to each category based on your priorities and financial goals.
- Review and adjust your budget regularly to ensure it remains aligned with your financial situation and goals.
Calculating Disposable Income and Savings Goals
Disposable income refers to the amount of money you have left after deducting taxes and other mandatory deductions from your gross income. This is the money you have available to spend or save.
Reading a pay stub answer key can be helpful to understand how your paycheck is calculated. If you’re studying for the AP Human Geography exam, you may also find it useful to practice with an ap human unit 1 practice test . This can help you get a better understanding of the concepts covered on the exam, including those related to income and employment.
Returning to the topic of pay stubs, it’s important to keep in mind that they can vary from employer to employer, so it’s always a good idea to refer to your specific pay stub for the most accurate information.
Disposable Income = Gross Income
- Taxes
- Mandatory Deductions
To determine your savings goals, consider your financial objectives (e.g., retirement, emergency fund, home purchase). Aim to save a specific percentage of your disposable income towards these goals.
Managing Expenses and Making Informed Decisions, Reading a pay stub answer key
- Identify areas where you can reduce expenses without compromising your essential needs.
- Negotiate lower bills (e.g., phone, internet) or consider switching to more affordable service providers.
- Explore ways to increase your income through side hustles, promotions, or additional skills.
- Seek professional financial advice if needed to optimize your financial planning and decision-making.
Additional Considerations
Understanding pay stubs involves not only knowing its components but also being aware of the legal and practical aspects surrounding them.
Legal Requirements
Pay stubs are legal documents that employers are required to provide to their employees by law. These regulations vary by country and state, but generally include the following information:
- Employee’s name and contact information
- Employer’s name and address
- Pay period dates
- Gross and net pay
- Deductions and withholdings
- Hours worked
- Pay rate
Resources for Employees
If you need assistance understanding your pay stub, several resources are available:
- Human Resources Department:Your company’s HR department can provide explanations and answer questions about your pay stub.
- Online Resources:Websites like the U.S. Department of Labor provide comprehensive guides and tools for understanding pay stubs.
- Financial Advisors:If you have complex financial needs, consider consulting a financial advisor for guidance on interpreting your pay stub.
Benefits of Digital Pay Stubs
In recent years, digital pay stubs have become increasingly popular. They offer several benefits over traditional paper stubs:
- Convenience:Digital pay stubs are accessible online, making them easy to view and manage.
- Security:They are less likely to be lost or stolen than paper stubs.
- Environmental Friendliness:They reduce paper waste and are more environmentally sustainable.
- Additional Features:Online portals often provide additional features, such as tax calculators and budgeting tools.
Q&A
What is the purpose of a pay stub?
A pay stub is a legal document that provides a detailed breakdown of an employee’s earnings, deductions, and net pay for a specific pay period.
What are the key sections of a pay stub?
The key sections of a pay stub typically include gross earnings, deductions, withholdings, net pay, and year-to-date earnings and deductions.
How can I use my pay stub to create a budget?
By tracking your earnings and expenses using your pay stub, you can create a budget that aligns with your financial goals and helps you manage your money effectively.